Understanding What Causes an Enlarged Uterus and How to Address It
An enlarged uterus is a condition where the uterus grows beyond its normal size, often leading to noticeable symptoms and health concerns. The causes can vary, ranging from benign growths to more complex medical issues. If you’ve ever wondered what causes an enlarged uterus, understanding the underlying factors is the first step toward seeking the right treatment.
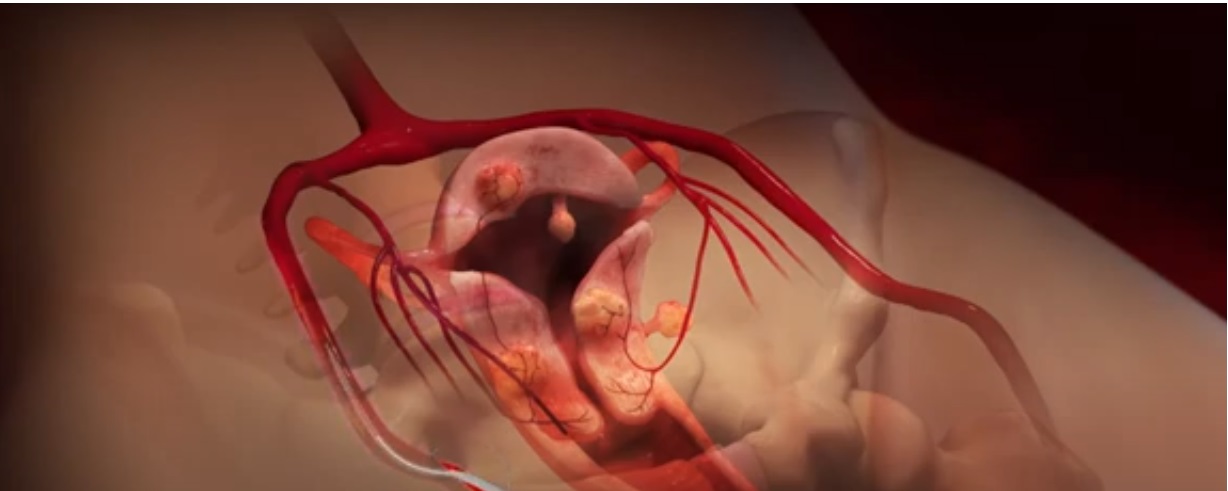
One of the most common causes of an enlarged uterus is uterine fibroids—noncancerous growths that develop within or on the uterus. Depending on their size and location, fibroids can significantly increase uterine volume and cause symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and bloating. Fibroids are most prevalent in women of reproductive age and may grow due to hormonal fluctuations, particularly estrogen and progesterone.
Another cause is adenomyosis, a condition where the uterine lining grows into the muscular wall of the uterus. This can make the uterus tender, enlarged, and prone to heavy, painful periods. Adenomyosis often occurs in women who have had children or undergone uterine surgery.
Pregnancy is a natural reason for an enlarged uterus, as it expands to accommodate the growing fetus. However, after childbirth, the uterus usually returns to its normal size. If it remains enlarged, further investigation is needed to rule out complications or underlying conditions.
Other potential factors include endometrial cancer, ovarian cysts, or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). While less common, these conditions can also lead to uterine enlargement and should be evaluated by a medical professional to ensure timely treatment.
Symptoms of an enlarged uterus can range from mild discomfort to severe pain and include irregular menstrual cycles, lower abdominal bloating, back pain, urinary frequency, and constipation. If you experience these symptoms, a healthcare provider can diagnose the cause using imaging techniques such as ultrasound or MRI, along with a detailed medical history and pelvic exam.
Treatment for an enlarged uterus depends on the underlying cause. Fibroids, for example, can be managed with non-invasive options like Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE), which targets the blood supply to fibroids, causing them to shrink. Other treatments might include hormonal therapy, minimally invasive procedures, or surgery in more severe cases.
Early detection and treatment can prevent complications and improve quality of life. By understanding what causes an enlarged uterus, you can make informed decisions about your reproductive health and choose treatment options that align with your personal needs.




